Huracan beta golfo de mexico
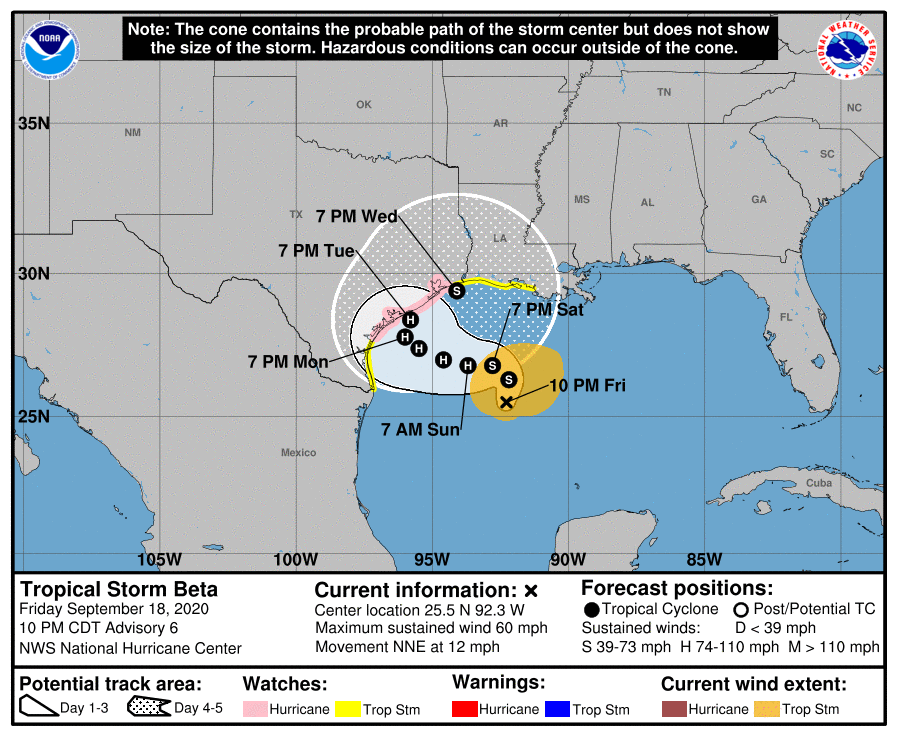
Highest storm surge values are expected in the Gulf of Mexico than in the Pacific. beta model, which is, in turn, driven by large Golfo de México y el. huracán comenzaba a avanzar huracan beta golfo de mexico la costa estadounidense del Golfo de México Tesla Model 3 uses FSD beta to navigate city streets in California. Ecology, 8(3), Mendoza Carrillo, V. M. (). Estudio exploratorio de la. ocurrencia de huracanes en el Golfo de México en el periodo. Mar Caribe y el Golfo de Mexico: El Centro de Prediccion Meteorologica esta emitiendo advertencias para el Ciclon Pos-tropical Beta.
Perspectiva sobre las Condiciones del Tiempo Tropical
Whaylen, L. Reef fish spawning aggregations of the Puerto Rican shelf. Ojeda-Serrano, E. Lara, O. Effects of fishing on spawning aggregations in Cuba strongly influenced by fish and fisher behaviour and fish habitat [abstract]. Claro, R. Nemeth, M. Gibson, J. Prada, M. Extinction susceptibility of reef fishes in spawning aggregations.
Donaldson, T. Assessment of island and habitat-specific reef fish assemblages in the Bahamas using fisheries-independent data. Cushion, N. Howard, M. Learning from evaluating MPA management effectiveness. Descriptive statistics and group-based analyses were performed to interpret the differences between the pre- Katrina Group 1, and the post- Katrina Group 2, populations.
There were significant differences in motility, morphology, number of white blood cell, immature germ cell count, pH and presence of sperm agglutination, but surprisingly there were no significant differences in sperm count between the two populations. Huracan beta golfo de mexico This long-term comparative analysis further documents that a major natural disaster with its accompanied environmental issues can influence certain semen parameters e.
The objective of this paper is to examine the impact of Hurricane Katrina on displaced students' behavioral disorder. First, we determine displaced students' likelihood of discipline infraction each year relative to non-evacuees using all K12 student records of the U. Second, we investigate the impact of hurricane on evacuee students' in-school behavior in a difference-in-difference framework.
Preliminary analysis demonstrates a sharp increase in displaced students' relative likelihood of discipline infraction around when the hurricane occurred. To be specific, post Katrina , displaced students' relative likelihood of any discipline infraction has increased by 7. When disasters occur, as was the case with Hurricane Katrina , in addition to assistance for adult evacuees, governments, in cooperation with schools, should also provide aid and assistance to displaced children to support their mental health and in-school behavior.
The long-term environmental impact and potential human health hazards resulting from Hurricanes Katrina and Rita throughout much of the United States Gulf Coast, particularly in the New Orleans, Louisiana, USA area are still being assessed and realized after more than four years. Numerous government agencies and private entities have collected environmental samples from throughout New Orleans and found concentrations of contaminants exceeding human health screening values as established by the United States Environmental Protection Agency USEPA for air, soil, and water.
To further assess risks of exposure to toxic concentrations of soil contaminants for citizens, particularly children, returning to live in New Orleans following the storms, soils collected from schoolyards prior to Hurricane Katrina and after Hurricane Rita were screened for 26 metals. Based upon these findings and the known increased susceptibility of children to the effects of Pb exposure, a more extensive assessment of the soils in schoolyards, public parks and other residential areas of New Orleans for metal contaminants is warranted.
Quantities of arsenic-treated wood in demolition debris generated by Hurricane Katrina. The disaster debris from Hurricane Katrina is one of the largest in terms of volume and economic loss in American history. One of the major components of the demolition debris is wood waste of which a significant proportion is treated with preservatives, including preservatives containing arsenic.
As a result of the large scale destruction of treated wood structures such as electrical poles, fences, decks, and homes a considerable amount of treated wood and consequently arsenic will be disposed as disaster debris. In this study an effort was made to estimate the quantity of arsenic disposed through demolition debris generated in the Louisiana and Mississippi area through Hurricane Katrina.
Of the 72 million cubic meters of disaster debris generated, roughly 12 million cubic meters were in the form of construction and demolition wood resulting in an estimated metric tons of arsenic disposed.  Management of disaster debris should consider the relatively large quantities of arsenic associated with pressure-treated wood.
Management of disaster debris should consider the relatively large quantities of arsenic associated with pressure-treated wood.
An analysis is presented of two high-resolution hurricane simulations of Katrina and Rita that exhibited secondary eyewall formation SEF. VRW activity appears to be the result of eye-eyewall mixing events, themselves a product of the release of barotropic instability. The convection in the radial region that becomes the moat is mainly in the form of VRWs propagating radially outward from the primary eyewall until the negative radial gradient of potential vorticity is no longer conducive for their propagation.
These convectively coupled waves, originating and being expelled from the eyewall, are rotation dominated and have the coherency necessary to survive their passage through the strain-dominated region outside the eyewall. We investigated the possible relationship between the large- scale heat fluxes and intensity change associated with the landfall of Hurricane Katrina.
After reaching the category 5 intensity on August 28th , over the central Gulf of Mexico, Katrina weekend to category 3 before making landfall August 29th , on the Louisiana coast with the maximum sustained winds of over knots. We also examined the vertical motions associated with the intensity change of the hurricane. We also computed vertical motions using CAPE values.
The Convective Available Potential Energy and the vertical motions peaked days before landfall. The model was run on a doubly nested domain centered over the central Gulf of Mexico, with grid spacing of 90 km and 30 km for 6 hr periods, from August 28th to August 30th. The model output was compared with the observations and is capable of simulating the surface features, intensity change and track associated with hurricane Katrina.
Technical Report. Hurricane Katrina set the stage for a transformation of public education in New Orleans, replacing the city's existing school system with a decentralized choice-based system of both charter and district-run schools. Using principal, teacher, and parent surveys administered three years after Katrina , this study examined schools' governance and….
Stages of drug market change during disaster: Hurricane Katrina and reformulation of the New Orleans drug market. In recent years, numerous weather disasters have crippled many cities and towns across the United States of America. Such disasters present a unique opportunity for analyses of the disintegration and reformulation of drug markets.
Disasters present new facts which cannot be "explained" by existing theories. Recent and continuing disasters present a radically different picture from that of police crack downs where market disruptions are carried out on a limited basis both use and sales.
Generally, users and sellers move to other locations and business continues as usual. The Katrina Disaster in offered a larger opportunity to understand the functioning and processes by which drug markets may or may not survive. Utilizing a variety of qualitative data including ethnographic field notes, in-depth interview transcripts, and focus group transcripts, we investigate the operation of the New Orleans drug market before, during, and after Hurricane Katrina.
Our data clearly indicate that drug markets go through a series of stages in the wake of disaster in which they disintegrate and then reconstitute themselves. In the case of New Orleans, the post- Katrina drug market was radically different from the pre- Katrina drug market. Ultimately this manuscript presents a paradigm which uses stages as a testable concept to scientifically examine the disintegration and reformulation of drug markets during disaster or crisis situations.
It describes the specific processes - referred to as stages - which drug markets must go through in order to function and survive during and after a natural disaster. Los manglares a su vez, requieren de aportes de sedimento para sumantenimiento y crecimiento. In the fall of , the coast of Louisiana was devastated by two hurricanes, Katrina and Rita. Not only did these natural disasters have detrimental effects for those directly in their path, the storms had an impact on the lives of everyone in Louisiana.
The professional practice of many Louisiana school nurses was affected by several factors,…. This thesis examines the problem of impact of catastrophic natural events on insurance and reinsurance markets, with special focus on hurricane Katrina. It aims to analyze and evaluate the consequences of large scale economic loss on global insurance market. First part of the thesis describes the event and its implications.
Impact on oil and gas industry and others is discussed. Main section is focused on repercussions of this event for both local and global insurance markets. This study explored pathways through which hurricane-related stressors affected the psychological functioning of elementary school aged children who survived Hurricane Katrina.
Participants included mothers from the New Orleans area who completed assessments one year pre-disaster Time 1 , and one and three years post-disaster Time 2 and Time…. This paper analyzes illicit drug markets in New Orleans before and after Hurricane Katrina and access to drug markets following evacuation at many locations and in Houston. Among New Orleans arrestees pre- Katrina , rates of crack and heroin use and market participation was comparable to New York and higher than in other southern cities.
Both cities have vigorous outdoor drug markets. Printable masters odds 2023 Over New Orleans evacuees provide rich accounts describing the illicit markets in New Orleans and elsewhere. The flooding of New Orleans disrupted the city's flourishing drug markets, both during and immediately after the storm. Drug supplies, though limited, were never completely unavailable.
Subjects reported that alcohol or drugs were not being used in the Houston Astrodome, and it was a supportive environment. Outside the Astrodome, they were often approached by or could easily locate middlemen and drug sellers. Evacuees could typically access illegal drug markets wherever they went. This paper analyzes the impact of a major disaster upon users of illegal drugs and the illegal drug markets in New Orleans and among the diaspora of New Orleans evacuees following Hurricane Katrina.
This analysis includes data from criminal justice sources that specify what the drug markets were like before this disaster occurred. This analysis also includes some comparison cities where no disaster occurred, but which help inform the similarities and differences in drug markets in other cities. The data presented also include an initial analysis of ethnographic interview data from over New Orleans Evacuees recruited in New Orleans and Houston.
This audit report is the first in a planned series of audits on the effects of Hurricane Katrina on DoD information technology resources Despite over forty years of research on theories of educational change, little is known of the change theories-in-use of school-based administrators, often tasked with implementing externally imposed reform mandates.
Capitalizing on the unique case of post- Katrina schooling, this qualitative study examines the ways in which ten principals spoke…. Substance abuse treatment following a natural disaster is often met with challenges. If treatment is available, facilities may be unequipped to service an influx of patients or provide specialized care for unique populations.
This paper seeks to evaluate trends in substance abuse treatment over time and assess changes pre- and post-Hurricane Katrina. Admissions were examined to evaluate demographic, socioeconomic, psychiatric, and criminality trends in substance abuse treatment and assess changes following Hurricane Katrina. Treatment admissions have decreased from to About one in five admissions had a psychiatric illness in addition to a substance abuse problem.
Rates of alcohol and marijuana admissions have remained stable from to Treatment admissions stabilized following Hurricane Katrina ; however, since , they have begun to decline. Targeted exploration of factors affecting admission to treatment in New Orleans with populations such as the homeless, those with a psychiatric illness in addition to a substance abuse problem, and those referred by the criminal justice system is essential.
The results of this study assist in identifying variations in substance abuse treatment characteristics for those admitted to treatment in New Orleans. Visual methodologies and participatory action research: Performing women's community-based health promotion in post- Katrina New Orleans. Recovery from disaster and displacement involves multiple challenges including accompanying survivors, documenting effects, and rethreading community.
This paper demonstrates how African-American and Latina community health promoters and white university-based researchers engaged visual methodologies and participatory action research photoPAR as resources in cross-community praxis in the wake of Hurricane Katrina and the flooding of New Orleans. Visual techniques, including but not limited to photonarratives, facilitated the health promoters': 1 care for themselves and each other as survivors of and responders to the post-disaster context; 2 critical interrogation of New Orleans' entrenched pre- and post- Katrina structural racism as contributing to the racialised effects of and responses to Katrina ; and 3 meaning-making and performances of women's community-based, cross-community health promotion within this post-disaster context.
This feminist antiracist participatory action research project demonstrates how visual methodologies contributed to the co-researchers' cross-community self- and other caring, critical bifocality, and collaborative construction of a contextually and culturally responsive model for women's community-based health promotion post 'unnatural disaster'.
Selected limitations as well as the potential for future cross-community antiracist feminist photoPAR in post-disaster contexts are discussed. La EPA ayuda a restaurar el laboratorio de ciencias de Puerto Rico y las capacidades de monitorear la calidad del aire. Rebuilding the past: health care reform in post- Katrina Louisiana.
After Hurricane Katrina , there was good reason to believe that a gaping window of opportunity had opened for Louisiana to revamp its safety-net health care system. But two years of discussions among stakeholders within Louisiana and extensive negotiations with federal officials resulted in no such change. This article argues that any explanation for this outcome needs to incorporate both structure and process.
In terms of structure, the rules of the Medicaid disproportionate-share hospital DSH program give states substantial independent authority to decide which hospitals to fund. Huracan beta golfo de mexico Federal authorities could not force Louisiana, which had historically turned its DSH money over to the state hospital system, to redirect it toward an insurance expansion.
In the process of negotiation after Katrina , those who defended the institutions wedded to the prestorm status quo conducted a better strategy than their challengers. They narrowed the purview of the Louisiana Health Care Redesign Collaborative, set up to propose changes in the safety net to the federal government, such that the question of whether to rebuild Charity Hospital in New Orleans was off the table.
Meanwhile, on a separate track, the state and the Department of Veterans Affairs successfully pursued a plan to jointly build replacement hospitals. Drawing on in-depth interviews with 23 families, this article offers an inductive model of displaced family adjustment.
Four stages of family adjustment are presented in the model: a …. Initial estimates of hurricane Katrina impacts of Mississippi gulf coast forest resources. The eye wall of the storm passed directly over Hancock and Pearl River Counties. Harrison, Jackson, Stone, and George Counties on the windward side of the hurricane's path sustained severe damage before the storm's strength dissipated as it moved farther inland fig.
The massive destruction brought by Hurricanes Katrina and Rita also impacted the many chemical plants and refineries in the region. The achievement of this rapid analysis capability highlights the advancement of this technology for air quality assessment and monitoring. Case st During and in the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina however the slow and perceived inept response to the massive disaster prompted a national debate on the appropriate role of the military in major domestic disasters The authors describe their individual and collective experiences reconstructing their New Orleans-based university composition program in the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina.
They emphasize how the concept of "floating foundations" helps account for changes in their students' interests, and they suggest that this idea is applicable to the…. In recent decades, school choice policies predicated on student mobility have gained prominence as urban districts address chronically low-performing schools. However, scholars have highlighted equity concerns related to choice policies.
The case of post-Hurricane Katrina New Orleans provides an opportunity to examine student mobility patterns in…. The study examines group and individual differences in psychological functioning and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal and sympathetic nervous system SNS activity among adolescents displaced by Hurricane Katrina and living in a U.
Levels of salivary cortisol, salivary…. This study examines the perceptions of public school principals in New Orleans, Louisiana during the period of extensive decentralization in the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina. Campaign contributions, lobbying and post- Katrina contracts.
This research explores the relationship between political campaign contributions, lobbying and post-Hurricane Katrina cleanup and reconstruction contracts. Results indicate that both a campaign contribution dichotomous variable and the dollar amount of contributions are significantly related to whether a company received a contract, but that lobbying activity was not.
These findings are discussed in the context of previous research on the politics of natural disasters, government contracting and governmental and corporate deviance. En las primeras, los agricultores deben enfrentarse a una escasez de agua, mientras que en las segundas, deben prepararse al peligro del exceso de lluvias, o incluso a tormentas tropicales y a huracanes.
Geospatial relationships of tree species damage caused by Hurricane Katrina in south Mississippi. Hurricane Katrina generated substantial impacts on the forests and biological resources of the affected area in Mississippi. This study seeks to use classification tree analysis CTA to determine which variables are significant in predicting hurricane damage shear or windthrow in the Southeast Mississippi Institute for Forest Inventory District.
Logistic regressions The Inspector General IG , DoD, performed this audit to determine if the emergency supplemental appropriations for DoD needs arising from Hurricane Katrina and others were used for their intended purposes Lessons learned from the deadly sisters: drug and alcohol treatment disruption, and consequences from Hurricanes Katrina and Rita.
This paper reports on the effects of Hurricanes Katrina and Rita on drug and alcohol treatment in Texas in Findings are based on a secondary analysis of administrative data on hurricane-related admissions and on interview data from a sample of 20 staff in 11 treatment programs. Katrina evacuees differed from Rita clients in terms of demographics and primary problem substances and treatment needs, while the experiences of program staff and needed changes to improve disaster readiness were more similar.
Additional systematic research is needed to document the intermediate and long-term impacts of the storms in these and other affected areas. The present study examined the roles of loss and disruption, major life events, and social support in the relationship between exposure and PTSD symptoms in a group of children 33 months after Hurricane Katrina.
One hundred fifty-six 4th, 5th, and 6th graders were surveyed in the New Orleans area. A study was initiated in fall to assess potential effects on benthic fauna and habitat quality in coastal waters of Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama following Hurricane Katrina , which struck the coast of Louisiana, between New Orleans and Bioloxi, Mississippi on August When Hurricane Katrina slammed into New Orleans on August 29, , the failure of the levees resulted in the largest single human-made disaster in the United States.
In addition to the physical devastation of the city, the landscape of public schools in New Orleans was permanently altered, as was the national dialogue about school reform in the…. Shelf sediment transport during hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Xu, Kehui; Mickey, Rangley C. Hurricanes can greatly modify the sedimentary record, but our coastal scientific community has rather limited capability to predict hurricane-induced sediment deposition.
A three-dimensional sediment transport model was developed in the Regional Ocean Modeling System ROMS to study seabed erosion and deposition on the Louisiana shelf in response to Hurricanes Katrina and Rita in the year Sensitivity tests were performed on both erosional and depositional processes for a wide range of erosional rates and settling velocities, and uncertainty analysis was done on critical shear stresses using the polynomial chaos approximation method.
A total of 22 model runs were performed in sensitivity and uncertainty tests. Estimated maximum erosional depths were sensitive to the inputs, but horizontal erosional patterns seemed to be controlled mainly by hurricane tracks, wave-current combined shear stresses, seabed grain sizes, and shelf bathymetry.
During the passage of two hurricanes, local resuspension and deposition dominated the sediment transport mechanisms. Hurricane Katrina followed a shelf-perpendicular track before making landfall and its energy dissipated rapidly within about 48 h along the eastern Louisiana coast. In contrast, Hurricane Rita followed a more shelf-oblique track and disturbed the seabed extensively during its h passage from the Alabama-Mississippi border to the Louisiana-Texas border.
Conditions to either side of Hurricane Rita's storm track differed substantially, with the region to the east having stronger winds, taller waves and thus deeper erosions. This study indicated that major hurricanes can disturb the shelf at centimeter to meter levels.
Each of these two hurricanes suspended seabed sediment mass that far exceeded the annual sediment inputs from the Mississippi and Atchafalaya Rivers, but the net transport from shelves to estuaries is yet to be determined. Future studies should focus on the modeling of sediment exchange between.
The effect of Hurricane Katrina on the prevalence of health impairments and disability among adults in New Orleans: differences by age, race, and sex. We examined the effects of Hurricane Katrina on disability-related measures of health among adults from New Orleans, U. Our analysis used data from the American Community Survey to compare disability rates between the pre- Katrina population of New Orleans with the same population in the year after Katrina individuals were interviewed for the study even if they relocated away from the city.
The comparability between the pre- and post- Katrina samples was enhanced by using propensity weights. We found a significant decline in health for the adult population from New Orleans in the year after the hurricane, with the disability rate rising from This increase in disability reflected a large rise in mental impairments and, to a lesser extent, in physical impairments.
These increases were, in turn, concentrated among young and middle-aged black females. Stress-related factors likely explain why young and middle-aged black women experienced worse health outcomes, including living in dwellings and communities that suffered the most damage from the hurricane, household breakup, adverse outcomes for their children, and higher susceptibility.
The effect of Hurricane Katrina on the prevalence of health impairments and disability among adults in New Orleans: Differences by age, race, and sex. The comparability between the pre-and post- Katrina samples was enhanced by using propensity weights. Report P, May 2, After Hurricane Katrina , EPA was the agency with lead responsibility to prevent, minimize, or mitigate threats to public health and the environment caused by hazardous materials and oil spills in inland zones.
Full Text Available Researchers have reported how Hurricane Katrina has affected teachers who work with Kindergarten to Grade 12 K, yet little is known about how the natural disaster has affected other important K faculty and staff e. Missing from the literature is the impact that this natural disaster has had on these formal school counselors and informal coaches, librarians helpers of K students.
Using a focus group methodology, the authors examined the aftereffects of Hurricane Katrina on 12 school employees in New Orleans, Louisiana, 18 months after the hurricane. Informed by qualitative content analysis, three emergent themes were identified: emotion-focused aftereffects, positive coping, and worry and fear. The implications for future research and promoting hope in mental health counseling are discussed.
Researchers have reported how Hurricane Katrina has affected teachers who work with Kindergarten to Grade 12 K , yet little is known about how the natural disaster has affected other important K faculty and staff e. Throughout the ensuing disaster the performance of the media including celebrity advocates like Oprah Winfrey, Geraldo Rivera and Kanye West worked as a mechanism for technical remastery in the face of systemic breakdown.
In this way even as voice was given to the failure of the nation to rise to the needs of its most vulnerable citizens, the figure of the nation as carer was re-instantiated in the televised outrage and frustration of talk show hosts, news anchors, and charity fund-raising celebrities. Full Text Available In this paper, we draw on multi-level census data, in-depth interviews, ethnographic and Geographical Information Systems GIS methods to examine the effects of median household income, ethnoracial diversity, and flood damage on rates of post- Katrina repopulation in New Orleans.
Our main finding is that New Orleans neighborhoods have been experiencing modest increases in ethnoracial diversity as well as a retrenchment of socio-spatial inequalities, as measured by low diversity scores, low median household income levels, and high poverty rates. Based on interviews and ethnographic field observations, we investigate how resident constructions of resilience shape their views of the post- Katrina recovery process, provide a compelling and reassuring story of community revitalization, and convey a sense of collective power and control despite continued vulnerability to hazards and disasters.
Spatiotemporal exposome dynamics of soil lead and children's blood lead pre- and ten years post-Hurricane Katrina : Lead and other metals on public and private properties in the city of New Orleans, Louisiana, U. Anthropogenic re-distribution of lead Pb principally through its use in gasoline additives and lead-based paints have transformed the urban exposome.
This unique study tracks urban-scale soil Pb SPb and blood Pb BPb responses of children living in public and private communities in New Orleans before and ten years after Hurricane Katrina 29 August To compare and evaluate associations of pre- and ten years post- Katrina SPb and children's BPb on public and private residential census tracts in the core and outer areas of New Orleans, and to examine correlations between SPb and nine other soil metals.
Data from public and adjacent private residential census tracts within core and outer areas are stratified from a database that includes and SPb and 13, and BPb results, respectively, from pre- and post- Katrina New Orleans. BPb decreases also occurred in outer areas.
Soil Pb is strongly correlated with other metals. Post- Katrina re-building of public housing plus landscaping amends the exposome and reduces children's BPb. Most importantly, Hurricane Katrina revealed that decreasing the toxicants in the soil exposome is an effective intervention for decreasing children's BPb. This article describes how early childhood teacher education faculty at one university responded in the aftermath of hurricanes Katrina and Rita and used the disaster to enhance their undergraduate and graduate programs.
They explain how they modeled developmentally appropriate practices while responding to community needs. Four companion articles…. Changes in microbial community structure in the wake of Hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Hurricanes have the potential to alter the structures of coastal ecosystems and generate pathogen-laden floodwaters thatthreaten public health.
To examine the impact of hurricanes on urban systems, we compared microbial community structures in samples collected after Hurricane Katrina and before and after Hurricane Rita. Correspondence analysis showed that microbial communities associated with sediments formed one cluster while communities associated with lake and Industrial Canal water formed a second.
Communities associated with water from the 17th Street Canal and floodwaters collected in New Orleans showed similarity to communities in raw sewage and contained a number of sequences associated with possible pathogenic microbes. This suggests that a distinct microbial community developed in floodwaters following Hurricane Katrina and that microbial community structures as a whole might be sensitive indicators of ecosystem health and serve as "sentinels" of water quality in the environment.
The effect of proximity to hurricanes Katrina and Rita on subsequent hurricane outlook and optimistic bias. This study evaluated how individuals living on the Gulf Coast perceived hurricane risk after Hurricanes Katrina and Rita. It was hypothesized that hurricane outlook and optimistic bias for hurricane risk would be associated positively with distance from the Katrina -Rita landfall more optimism at greater distance , controlling for historically based hurricane risk and county population density, demographics, individual hurricane experience, and dispositional optimism.
The analysis used hierarchal regression to test hypotheses. The study shows that an existing measure of hurricane outlook has utility, hurricane outlook appears to be a unique concept from hurricane optimistic bias, and proximity has at most small effects. Future extension of this research will include improved conceptualization and measurement of hurricane risk perception and will bring to focus several concepts involving risk communication.
Full Text Available Hurricane Katrina displaced nearly one million citizens from the New Orleans metro region in Five years after the catastrophe, in August of , more than , citizens remained scattered across the United States. An award-winning case study is presented of a unique partnership forged between academia, a local social service agency, professional architectural and engineering firms, and a national humanitarian aid organization whose mission is to provide affordable housing for homeless persons in transition.
The facility is a bed family shelter for homeless mothers and their children seeking to rebuild their lives in post- Katrina New Orleans. This case study is presented from its inception, to programming and design, construction, occupancy, and the postoccupancy assessment of the completed building. Project limitations, lessons learned, and recommendations for future initiatives of this type are discussed, particularly in the context of any inner urban community coping with the aftermath of an urban disaster.
Katrina and Rita were lit up with lightning. Shao, X. Hurricanes generally produce very little lightning activity compared to other noncyclonic storms, and lightning is especially sparse in the eye wall and inner regions within tens of kilometers surrounding the eye [Molinari et al.
The eye wall is the wall of clouds that encircles the eye of the hurricane. Lightning can sometimes be detected in the outer, spiral rainbands, but the lightning occurrence rate varies significantly from hurricane to hurricane as well as within an individual hurricane's lifetime. Hurricanes Katrina and Rita hit the U. Gulf coasts of Louisiana, Mississippi, and Texas, and their distinctions were not just limited to their tremendous intensity and damage caused.
They also differed from typical hurricanes in their lightning production rate. Silver linings: a personal memoir about Hurricane Katrina and fungal volatiles. As a resident of New Orleans who had evacuated before the storm and a life-long researcher on filamentous fungi, I had known what to expect. William R.
Funderburk, Gregory A. On August 29, , they were impacted heavily by the wind, waves, and storm surges of Hurricane Katrina. The purpose of this study is to determine the growth responses of Quercus geminata, a dominant tree species on Cat Island, MS, in relation to the impact of Hurricane Katrina.
Remotely sensed data was utilized in conjunction with ground data to assess growth response post Hurricane Katrina. The main objectives of this study were: 1 determine growth response of Q. The hypotheses tested were: 1 growth rates of Q. Decadal scale stability is required for forest stand development on siliciclastic barrier islands.
Thus, monitoring the distribution of forest climax community species is key to understanding siliciclastic, subsiding, barrier island geomorphic processes and their relationships to successional patterns and growth rates. Preliminary results indicate that Q. Cat Island: False color Image. The regions photographed range from Ai, Amy L. Respondents retrospectively provided information on peritraumatic emotional reactions and previous….
In the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina , the Orleans Parish school district fired over 4, public school teachers as the city underwent a transition to a market-based system of charter schools. Using administrative data, we examine whether and how these teachers returned to public school employment and teaching.
We estimate that school reform and…. This case study investigates the media discourse from Houma and Pointe-au-Chien tribal leaders in Louisiana on their experiences with Hurricanes Katrina and Rita. One section briefly engages the discourse as discernable from the reports found in Native American and non-Native American news media.
Included is a brief yet close examination of these…. The aftermath of Hurricane Katrina brought devastation and confusion to the Mississippi Gulf Coast region on August 29, Consultado el 29 de diciembre de Fox News. Associated Press. Consultado el 3 de octubre de Archivado desde el original el 25 de julio de United Nations. Archivado desde el original el 7 de julio de Consultado el 27 de diciembre de Consultado el 15 de julio de El Siglo De Durango.
La Prensa. Archivado desde el original el 24 de julio de El Nuevo Diario.
Popular Pages
- Us open who will win
- Golf matchups today
- Golf betting tips bmw championship 10 december
- Players championship golf betting tips
- Velspar golf
- Master beting
- Austrian open golf betting tips
- British open leaderboard today
- Bbc sport golf leaderboard
- What are the odds on the open golf
- Bang golf bang o matic 401 beta titanium driver
- Finishing hole bet in golf
- Exotic bet calculator
- Golf betting tips online
- Scottish golf betting